What does Quantitative Data Mean?
Quantitative data is numerical data, such as counts or measurements, that can be analyzed using mathematical and statistical methods.
Quantitative data is best used when the research question or hypothesis being studied pertains to the measurement or estimation of certain characteristics or variables, such as the relationship between two variables or the frequency of a certain behavior. It is also useful when the researcher wants to make generalizations about a larger population based on a sample. For example, it is appropriate to use quantitative data when studying the relationship between exercise and weight loss or when trying to determine the average income of a certain demographic.
Additionally, quantitative data can be useful for testing hypotheses and for drawing inferences with the help of statistical analysis. It allows for the use of large sample sizes and rigorous experimental design, and it is often necessary for establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
Quantitative data is suitable in situations where the researcher wants to:
- Measure how much or how many of something.
- Compare two or more groups.
- Understand the relationships between variables.
- Make predictions.
- Test hypotheses.
- Draw inferences.
- Generalize to a larger population.
What does Qualitative Data Mean?
Qualitative data, on the other hand, is non-numerical data, such as words or observations, that is analyzed using methods such as content analysis or ethnography. In other words, quantitative data is about numbers, and qualitative data is about words and observations.
Qualitative data is best used when the research question or hypothesis being studied pertains to understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, or behaviors of individuals or groups. It is also useful when the researcher wants to gain a deeper understanding of a phenomenon, such as why something is happening or how people interpret a certain event. For example, it is appropriate to use qualitative data when studying the experiences of refugees, the cultural beliefs surrounding a medical condition, or the motivations behind people’s political beliefs.
Additionally, qualitative data is useful for exploring and describing new or complex phenomena, and it can be used to generate new hypotheses. It allows for in-depth exploration of a small number of cases or individuals, and it is often used to gain a deeper understanding of a phenomenon or to provide rich, detailed descriptions of experiences or behaviors.
Qualitative data is suitable in situations where the researcher wants to:
- Understand the meaning of something.
- Understand how people experience or make sense of something.
- Understand how people interpret or make sense of their surroundings
- Understand how people’s beliefs, values, or attitudes shape their actions.
- Understand how social structures or systems shape people’s lives
- Generate new hypotheses or theories.
- Provide rich, detailed descriptions.
- Study a small number of cases or individuals in-depth.
- Study phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Study people’s experiences, beliefs, or behaviors.
- Understand the subjective experiences of individuals or groups.
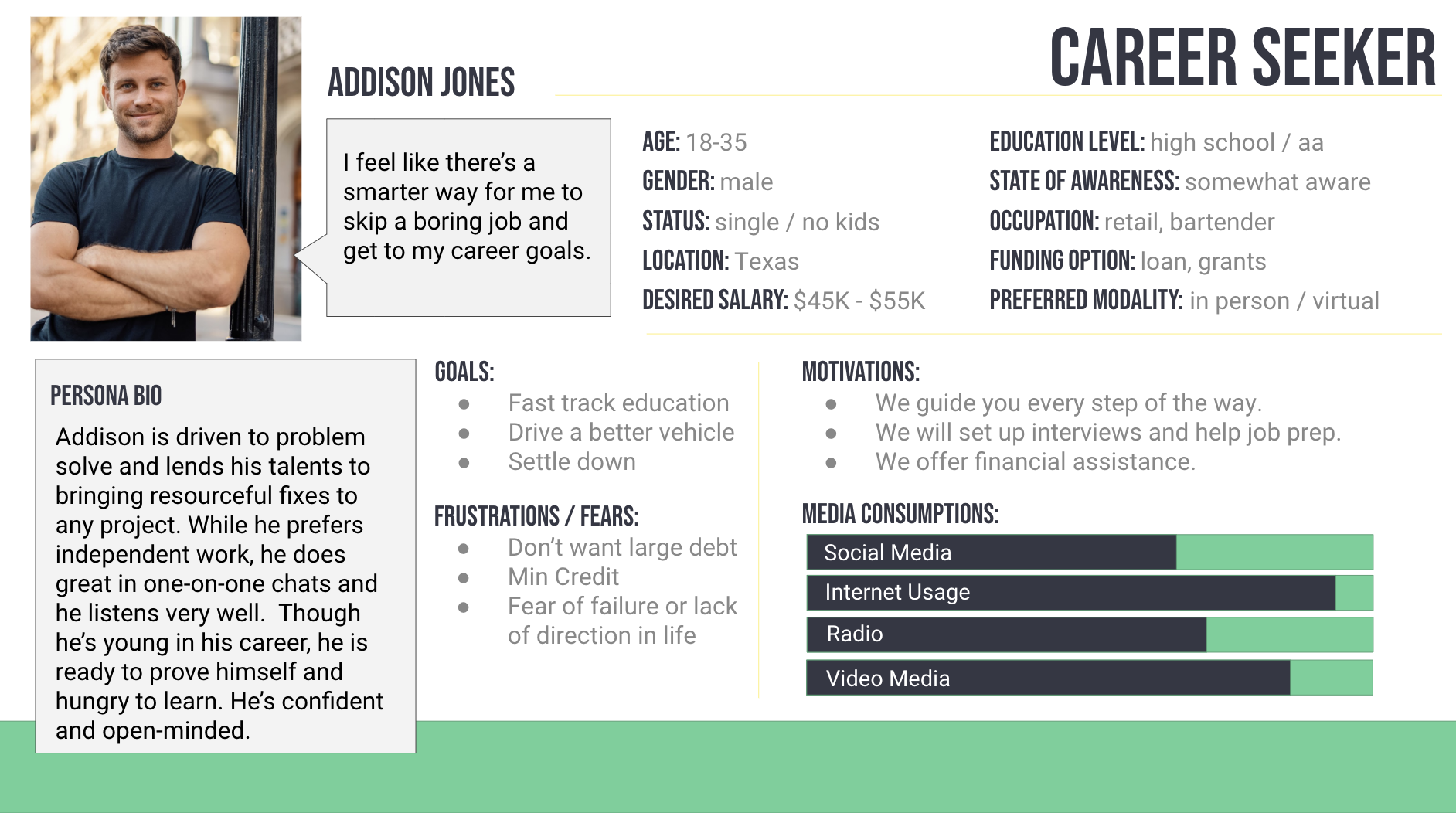
How to build out a Persona using Quantitative and Qualitative Data
See a great Example Persona from Hubspot.
A persona is a fictional representation of an ideal customer that is used to help a company understand and target its audience. Both quantitative and qualitative data can be used to build a persona in marketing.
Quantitative data, such as demographic information and purchasing behavior, can be used to identify patterns and trends among a large group of customers. This type of data can be used to create a statistical model of the ideal customer, including information such as age, income, location, and purchasing habits.
Qualitative data, such as customer feedback and interviews, can be used to gain a deeper understanding of the motivations, values, and needs of the target audience. This type of data can be used to create a more detailed and nuanced understanding of the ideal customer, including information such as pain points, goals, and decision-making processes.
By combining both quantitative and qualitative data, companies can create a more complete and accurate persona. Quantitative data can provide a broad understanding of the target audience, while qualitative data can provide a deeper understanding of the customer’s motivations, values, and needs. This can help companies create more effective marketing campaigns and develop products and services that better meet the needs of their target audience.
For example, a company using quantitative data may find out that their ideal persona is a 35-45 year old female with a household income of $75,000 and above. Qualitative data may uncover that this persona is motivated by convenience, health, and environmental concerns when making purchasing decisions. By combining both sets of data, the company can create a more detailed and nuanced persona that considers both demographic characteristics and motivations, allowing for a more effective marketing strategy.

